[Drug Name]
Common name: Amikacin Sulfate Injection
[Ingredients]
Main ingredient: Amikacin sulfate
Chemical name: O-3-Amino-3-deoxygenation- α- D-glucopyranosyl - (1 → 6) - O - [6-amino-6-deoxy- α- D-glucopyranosyl - (1 → 4)] - N - (4-amino-2-hydroxy-1-oxybutyl) -2-deoxy-D-streptomycin sulfate.
Chemical structural formula: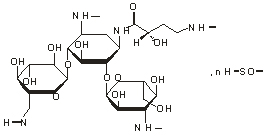
Molecular formula: C22H43N5O13 · nH2SO4 (n=1.8 or 2)
Molecular weight: 762.15 (n=1.8) or 781.76 (n=2)
All excipients: sodium citrate, sodium sulfite.
[Character]This product is a colorless to slightly yellow clear liquid.
[Indications]This product is suitable for severe infections caused by sensitive gram-negative bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and some other pseudomonas, Escherichia coli, Proteus, Klebsiella, Enterobacteriaceae, Serratia, Acinetobacter, and Staphylococcus (methicillin sensitive strains), such as bacteremia or septicemia, bacterial endocarditis, lower respiratory tract infection, bone and joint infection, biliary tract infection, abdominal infection, complex urinary tract infection Skin and soft tissue infections, etc. Due to its stability towards most aminoglycoside inactivating enzymes, this product is particularly suitable for treating severe infections caused by Gram negative bacteria resistant to kanamycin, gentamicin, or tobramycin.
[Specification]2ml:0.2g
[Usage dosage]1. Adult, intramuscular injection or intravenous drip. Patients with simple urinary tract infections who are resistant to commonly used antibiotics receive 0.2g (1 dose) every 12 hours; For other systemic infections, 7.5mg/kg every 12 hours or 15mg/kg every 24 hours. Adults should not exceed 1.5g per day and the treatment period should not exceed 10 days. 2. Children, intramuscular injection or intravenous drip. The first dose is 10mg/kg body weight, followed by 7.5mg/kg every 12 hours or 15mg/kg every 24 hours. 3. Patients with renal dysfunction: those with a creatinine clearance rate>50-90ml/min should receive 60-90% of the normal dose (7.5mg/Kg) every 12 hours; For those with a creatinine clearance rate of 10-50ml/min, use 20-30% of 7.5mg/kg every 24-48 hours. The creatinine clearance rate can be directly measured or calculated from the blood creatinine value using the following formula:
(140 years old) × Standard weight (kg)
Adult male creatinine clearance rate=--------------------------
72 × Patient blood creatinine concentration (mg/dl)
(140 years old) × Standard weight (kg)
Perhaps-------------------------
50 × Patient blood creatinine concentration( μ Mol/L)
(140 years old) × Standard weight (kg)
Adult female creatinine clearance rate=--------------------------×0.85
72 × Patient blood creatinine concentration (mg/dl)
(140 years old) × Standard weight (kg)
或-------------------------×0.85
50 × Patient blood creatinine concentration( μ Mol/L)
[Adverse reactions]
1. Patients may experience hearing loss, tinnitus, or a feeling of fullness in the ears; A few patients may also experience symptoms such as dizziness and unstable walking. Hearing loss generally does not worsen after stopping medication, but some individuals may continue to develop into deafness after stopping medication.
2. This product has a certain degree of nephrotoxicity, and patients may experience hematuria, reduced urination frequency or urine output, increased blood urea nitrogen, and creatinine levels. Most cases are reversible, with immediate relief after discontinuation of medication, but there are also individual reports of renal failure.
3. Neuromuscular blockade effects such as weakness, drowsiness, and difficulty breathing are rare.
4. Other adverse reactions include headache, numbness, needle infection, tremor, convulsions, joint pain, drug fever, eosinophilia, abnormal liver function, blurred vision, etc.
[Taboo]Patients with allergies to amikacin or other aminoglycosides are prohibited.
[Precautions]
1. Cross allergy: Patients who are allergic to one type of aminoglycoside may also be allergic to other aminoglycosides.
During the medication process, attention should be paid to the following examinations:
(1) Urinary routine and renal function testing to prevent severe nephrotoxic reactions.
(2) Hearing tests or audiogram tests, with particular attention to high-frequency hearing damage, are particularly important for elderly patients.
3. When conditions permit during the course of treatment, blood drug concentrations should be monitored, especially in newborns, elderly people, and patients with renal dysfunction. The peak blood concentration (Cmax) of 7.5mg/kg administered every 12 hours should be maintained between 15-30 μ G/ml, valley concentration 5-10 μ G/ml; The peak blood concentration of 15mg/kg administered once a day should be maintained at 56-64 μ G/ml, valley concentration should be<1 μ G/ml.
4. This product should be used with caution in the following situations:
(1) Dehydration can increase blood drug concentration and lead to toxic reactions;
(2) The 8th pair of brain nerve damage, as this product can cause damage to the vestibular and auditory nerves;
(3) Myasthenia gravis or Parkinson's disease, which can cause neuromuscular blockade and lead to skeletal muscle weakness;
(4) Patients with renal function impairment may have nephrotoxicity due to this product.
5. Interference with diagnosis: This product can increase the measured values of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), serum bilirubin concentration, and lactate dehydrogenase concentration; The measured values of blood calcium, magnesium, potassium, and sodium concentrations may decrease.
6. Aminoglycosides and β Lactam (cephalosporins and penicillins) can inactivate each other when mixed. When this product is used in combination with the aforementioned antibiotics, it must be dripped in separate bottles. Amikacin should not be administered in the same bottle as other drugs.
7. Patients should be given sufficient water to reduce renal tubular damage.
When preparing intravenous medication, add 100-200ml of sodium chloride injection, 5% glucose injection, or other sterile diluents every 500mg. Adults should slowly drip within 30-60 minutes, and the amount of diluted liquid in infant patients should be correspondingly reduced.
[Medication for pregnant lactating women]This product belongs to Class D for pregnant women, which poses a certain risk to humans, but the benefits may outweigh the disadvantages after use. This product can pass through the placenta and reach fetal tissue, which may cause fetal hearing damage. Pregnant women must fully weigh the pros and cons before using this product. Breastfeeding women should pause breastfeeding when taking medication.
[Children's medication]Aminoglycosides should be used with caution in pediatrics, especially in premature infants and newborns where the renal tissue is not fully developed, which prolongs the half-life of these drugs and makes them prone to accumulation and toxic reactions in the body.
[Elderly medication]Elderly patients have a certain degree of physiological decline in renal function, and even if the measured values of renal function are within the normal range, a smaller treatment dose should still be used. Elderly patients are prone to various toxic reactions after using this product, and blood drug concentrations should be monitored as much as possible during the treatment period.
[Drug interactions]
1. This product can increase ototoxicity, nephrotoxicity and neuromuscular blocking effect when used in combination with other aminoglycosides or applied locally or systematically successively.
2. When combined with neuromuscular blockers, this product can exacerbate neuromuscular blockade, leading to symptoms such as muscle weakness and respiratory depression. The combination of this product with capreomycin, cisplatin, etaniac acid, furosemide or vancomycin (or norvancomycin), or continuous local or systemic application may increase ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity.
3. Local or systemic use of this product in combination with cephalothiophene or cefazolin may increase renal toxicity. This product should not be compatible with injections such as amphotericin B, cephalothiophene, sulfadiazine, and tetracycline, and should not be dripped in the same bottle.
4. This product can increase nephrotoxicity and neuromuscular blockade when used in combination with polymyxin injections or continuously applied locally or throughout the body.
5. Other nephrotoxic drugs and ototoxicity drugs should not be used together or successively with this product to avoid aggravating nephrotoxicity or ototoxicity.
[Drug overdose]Due to the lack of specific antagonists, when this product is overdosed or causes toxic reactions, symptomatic and supportive therapies are mainly used, while replenishing a large amount of water. Hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis can help clear amikacin from the blood.
[Pharmacological toxicity]Amikacin sulfate is an aminoglycoside antibiotic. This product has good effects on most Enterobacteriaceae bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, Enterobacteriaceae, Proteus, Shigella, Salmonella, Citrobacter, Serratia, etc., and also has good effects on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and some other pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, Alcaligenes, etc; It also has good antibacterial activity against meningococcus, gonococcus, influenza bacillus, Yersinia, Campylobacter foetus, tubercle bacillus and some Mycobacterium, and its antibacterial activity is slightly lower than that of gentamicin. The most prominent advantage of this product is its stability towards the aminoglycoside inactivating enzymes produced by many gut Gram negative bacteria, and it will not lose antibacterial activity due to the inactivation of these enzymes. Among the 12 inactivating enzymes currently isolated, this product can only be inactivated by AAC (6 '). In addition, AAD (4') and APH (3 ') - III can occasionally cause moderate bacterial resistance to this product. About 60-70% of clinically isolated Enterobacteriaceae bacteria resistant to aminoglycosides such as gentamicin, tobramycin and netilmicin are still sensitive to this product. In recent years, there has also been an increase in Gram negative bacteria resistant to amikacin. Among gram-positive cocci, this product has good antibacterial effect against methicillin sensitive strains in Staphylococcus, and most of Streptococcus pneumoniae, streptococci in each group and Enterococcus are resistant to it. This product is not effective against anaerobic bacteria. The mechanism of action of this product is that it acts on the 3OS subunit of bacterial ribosome and inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. Amikacin often exhibits synergistic antibacterial effects when used in combination with semi synthetic penicillin or cephalosporins.
[Pharmacokinetics]Amikacin is rarely absorbed orally. After intramuscular injection, it is quickly absorbed. It is mainly distributed in extracellular fluid, and some drugs can be distributed to various tissues, and can be accumulated in renal cortical cells and inner ear fluid; But the concentration in the heart's ear tissue, pericardial fluid, muscle, fat, and interstitial fluid is very low. Low concentrations of bronchial secretions, bile, and aqueous humor. The protein binding rate is low. Not metabolized in the body. Adult blood elimination half-life (t1/2 β) It takes 2-2.5 hours. It can enter fetal tissue through the placenta. Low concentration in cerebrospinal fluid. Mainly excreted through glomerular filtration, over 90% is excreted within 24 hours after administration. Hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis can remove a considerable amount of drugs from the blood, thereby significantly shortening the half-life.
[Storage]Sealed and stored in a cool and dark place (avoiding light and not exceeding 20 ℃).
[Packaging]Ampoule packaging, 10 pieces/box
[Validity period]24 months
[Executive Standards]Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2010 Edition Part 2
[Approval number]National Pharmaceutical Standards H33021538
[Manufacturing enterprise]
Enterprise Name:Zhejiang Cheng Yi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Production Address: No.118 Huahua Road, Dongtou County, Zhejiang Province, China
Phone number:86-0577-6348-3979
Fax number:86-0577-6348-5135
Website:en.chengyipharma.com