[Drug Name]
Common name: Tolasemide Injection
Product name: Li Quan
[Ingredients]
Main ingredients: Tolasemide
Chemical name: 1-isopropyl-3- [(4-m-toluenamino-3-pyridyl) sulfonyl group] urea
Chemical structural formula: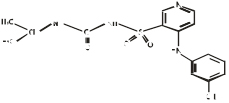
Molecular formula: C16H20N4O3S
Molecular weight: 348.43
All auxiliary materials: polyethylene glycol 400, sodium hydroxide.
[Character]This product is a colorless or almost colorless clear liquid.
[Indications]Suitable for patients with congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, ascites, and edema caused by kidney disease who require rapid diuresis or cannot take diuretics orally.
[Specification]2m1:l0mg
[Usage dosage]Edema and cirrhosis ascites caused by congestive heart failure: Generally, the initial dose is 5mg (half dose) or 10mg (1 dose), once a day, slowly injected intravenously, or diluted with 5% glucose solution or physiological saline before intravenous infusion; If the therapeutic effect is not satisfactory, the dosage can be increased to 20mg (2 doses) once a day, with a maximum daily dose of 40mg (4 doses), and the treatment course should not exceed one week. Edema caused by kidney disease, with an initial dose of 20mg (2 tubes) once a day, can be gradually increased to the maximum dose of 100mg (10 tubes) per day as needed, with a course of treatment not exceeding one week.
[Adverse reactions]The common adverse reactions included headache, dizziness, fatigue, anorexia, muscle spasm, nausea and vomiting, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, constipation and diarrhea; Long term and extensive use may lead to water and electrolyte imbalance. In the early stages of treatment and in older patients, polyuria often occurs. Some patients may experience hypotension, mental disorders, thrombotic complications due to blood concentration, as well as arrhythmia, angina, acute myocardial infarction, or fainting caused by heart or cerebral ischemia. Hypokalemia can occur in patients with low potassium diet, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive use of laxatives, and abnormal liver function. Individual patients may experience skin allergies, occasional itching, rash, photosensitive reactions, rare cases of dry mouth, abnormal limb sensation, and visual impairment.
[Taboo]Patients with renal failure and anuria, pre liver coma or liver coma, allergic to this product or sulfonylurea, hypotension, hypovolemia, hypokalemia or hyponatremia, and severe difficulty urinating (such as prostate enlargement) should not use this product.
[Precautions]
1. Users of this product should regularly check for electrolytes (especially blood potassium), blood sugar, uric acid, creatinine, blood lipids, etc.
2. Before starting treatment with this product, urinary disorders must be corrected, especially for elderly patients or those at the beginning of treatment who need to carefully monitor electrolyte and blood volume deficiencies and symptoms related to blood concentration.
3. Patients with liver cirrhosis and ascites who use this product for diuresis should be hospitalized for treatment. If these patients urinate too quickly, it can cause serious electrolyte disorders and liver coma.
4. This product can be used in combination with aldosterone antagonists or potassium sparing drugs to prevent hypokalemia and metabolic alkalosis.
5. Patients with hypertrophy of prostate have difficulty in urination, and the use of this product can lead to urinary retention and bladder dilatation.
6. When starting treatment with this product or switching from other medications to using this product or starting a new adjuvant medication, individual patients' alertness is affected (such as when driving a vehicle or operating a machine).
7. This product must be slowly injected intravenously. It should not be mixed with other drugs before intravenous injection, but can be diluted with physiological saline or 5% glucose solution as needed.
8. If long-term medication is required, it is recommended to switch from intravenous administration to oral administration as soon as possible. The duration of intravenous administration is limited to one week.
[Medication for pregnant lactating women]It is not recommended for pregnant and lactating women to use this product.
[Children's medication]It is not yet clear whether it is safe and effective for pediatric patients.
[Elderly medication]The efficacy and safety of using this product in elderly patients are no different from those in young people, but in the early stages of using this product, elderly patients should pay special attention to monitoring blood pressure, electrolytes, and whether they have difficulty urinating.
[Drug interactions]
1. The low potassium caused by this product can exacerbate the adverse reactions of cardiac glycosides.
2. This product can enhance the potassium consumption effect of salt, glucocorticoids, and laxatives.
3. Non steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (such as indomethacin) and probenecid can reduce the diuretic and antihypertensive effects of this product.
4. This product can enhance the effect of antihypertensive drugs.
5. Continuous use of this product or starting to combine it with an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor may cause excessive blood pressure reduction.
6. This product can reduce the effect of anti diabetes drugs.
7. At high doses, it may aggravate the ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics (such as kanamycin, gentamicin, tobramycin), cisplatin preparations and cephalosporins.
8. This product can enhance the effects of arrow like muscle relaxants and theophylline drugs.
9. This product can reduce the effects of norepinephrine and adrenaline.
10. When patients use high-dose salicylates, this product can increase the toxicity of salicylates.
[Drug overdose]When excessive medication occurs, the loss of body fluids and electrolytes may lead to drowsiness, electrolyte disorders, and gastrointestinal symptoms. Treatment: Targeted and supportive therapy, timely supplementation of body fluids and electrolytes, and dynamic monitoring of electrolytes.
[Pharmacology toxicology]Mechanism of action: This product is a sulfonylurea pyridine diuretic that acts on the thick segment of the ascending branch of the Henry's medullary loop, inhibiting the Na+/K+/2Cl carrier system and increasing the excretion of Na+, K+, Cl -, and water in urine. However, it has no significant effect on glomerular filtration rate, renal plasma flow, or acid-base balance in the body. Pharmacodynamics: This product has strong diuretic effects on both rats and dogs. In these two animals, there is a linear relationship between urine volume, urine electrolyte excretion, and the logarithm of dose. The minimum effective dose of this product is 0.2mg/kg for rats, less than 0.1mg/kg for dogs, and the maximum effective dose is about 10mg/kg. In terms of pharmacological weight, the diuretic effect of this product on rats is 9-40 times that of furosemide, and 10 times that on dogs. The diuretic effect lasts for about 2 hours in rats, while it lasts for more than 8 hours in dogs. The diuretic effect of this product is not weakened in rats who take 10mg/kg orally daily for 15 days. The systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure, mean blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, respiratory pressure and electrocardiogram were not significantly affected by intravenous injection of tolasemide 1, 3 and 10 mg/kg in dogs. The lifetime carcinogenicity test of carcinogenic rats and mice showed no increase in tumor incidence after administration of this product at 9mg/kg/day and 32mg/kg/day, respectively. Based on body weight, this dose is 27-96 times the human dose of 20mg; Based on a body surface area of 5-8 times. The mutagenic tolasemide and its main metabolites were tested by bacterial Ames test, chromosome aberration and human lymphoid sister chromatid exchange test, bone marrow cell nuclear abnormality test of hamsters and mice, and unconventional DNA synthesis test of mice and rats. The results of in vivo and in vitro tests showed no mutagenicity. There was no adverse effect on reproductive performance when the dose of reproductive toxicity was 25mg/kg/day for female and male rats. There is no fetal toxicity or teratogenic effect at a dose of 5mg/kg/day in rats or 1.6mg/kg/day in rabbits. When the doses of rats and rabbits were greater than 5 and 4 times, respectively, the average body weight of the fetus and mother decreased, and the delay in fetal absorption and ossification increased. Long term toxicity: Oral administration of 0.2, 1, 5, and 25mg/kg of tolasemide to rats for 12 consecutive months. The weight gain of the group with a dose of 5mg/kg or above was inhibited, with a decrease in total protein and Cl -, an increase in BUN, and a granular appearance on the surface of the kidney. Pathological examination showed that the renal tubules were dilated with cell infiltration and fibrosis, while the K+of the 25mg/kg group decreased. Dogs took oral tolasemide at doses of 0.0l, 0.08, and 0.4mg/kg/day for 12 consecutive months. In the 0.4mg/kg dose group, all male dogs had nasal dryness. Pathological examination showed renal tubular degeneration, dilation, cell infiltration, calcium deposition, and fibrosis in the male dog 0.4mg/kg group and the female dog group above 0.08mg/kg. Auditory, ophthalmic, physiological, renal function, and other examinations showed no changes related to this product.
[Pharmacokinetics]After 1 hour of intravenous infusion of 20mg of this product, the blood drug concentration of this product reached 3.18mg/L in healthy volunteers. The peak time of metabolites M1 and M5 is 1-2 hours, and their amounts are 3.5% and 27.4% of the original drug, respectively. Its elimination half-life is 3.5 hours. The distribution volume of this product in healthy adults, patients with mild to moderate renal failure and congestive heart failure is 12-15L, and the distribution volume in patients with liver cirrhosis is approximately doubled. Research on the tissue distribution of radioactive markers showed that the highest levels of radioactivity were observed in various tissues of rats after a single administration of this product for 0.5 to 1 hour. The highest levels were observed in the liver and kidneys, but lower than in plasma. After 72 hours, the radioactivity in each tissue was lower than the detection level. There was no significant difference in the comparative radioactivity between the tissues after 14 and 1 doses. Pregnant rats can enter the fetus after administration, and the highest concentration is reached 6 hours after administration, which gradually decreases thereafter. The plasma protein binding rate is>99%. 80% of this product is metabolized in the liver, with the main metabolites being inactive carboxylic acid derivatives. 20% is excreted through the kidneys. Special population: Elderly people, except for those with decreased renal function and decreased renal clearance rate, generally have similar pharmacokinetic processes as young subjects. In patients with decompensated congestive heart failure, the liver and kidney clearance rates decreased after the use of tolasemide, possibly due to reduced liver congestion and renal blood flow, respectively. The total clearance rate of tolasemide is approximately 50% of that of healthy volunteers, with an increase in plasma half-life and AUC values. Due to the reduced renal clearance rate, only a small amount of this product can enter the site of action in the medullary loop, so its sodium excretion effect on patients with congestive heart failure is lower than that of healthy volunteers. When renal function is impaired, this product can be compensated through liver metabolic pathways, so the total plasma clearance rate and elimination half-life of patients with renal function impairment can still be maintained within the normal range. The distribution volume, plasma half-life, and renal clearance rate of patients with liver cirrhosis increased, but the total clearance rate remained unchanged.
[Storage]Keep away from light, sealed, and stored in a cool place (not exceeding 20 ℃).
[Packaging]Ampoule packaging, 10 pieces/box
[Validity period]Tentative 24 months
[Executive Standards]YBH18992005
[Approval number]National Pharmaceutical Standards H20051396
[Manufacturing enterprise]
Enterprise Name:Zhejiang Cheng Yi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Production Address: No.118 Huahua Road, Dongtou County, Zhejiang Province, China
Phone number:86-0577-6348-3979
Fax number:86-0577-6348-5135
Website:en.chengyipharma.com