[Drug Name]
Common name:Vitamin C Injection
[Ingredients]
Main ingredient: Vitamin C
Chemical name: L-ascorbic acid
Chemical structural formula: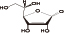
Molecular formula: C6H8O6
Molecular weight: 176.13
All auxiliary materials: sodium metabisulfite, sodium bicarbonate, EDTA-2Na.
[Character]This product is a colorless to slightly yellow clear liquid.
[Indications]
1. Used for the treatment of scurvy, as well as for various acute and chronic infectious diseases and auxiliary treatments such as epilepsy.
2. Treatment of chronic iron poisoning: Vitamin C promotes the chelation of iron by desferriamine, accelerating iron excretion.
3. Treatment of idiopathic methemoglobinemia.
4. The following situations increase the demand for vitamin C:
(1) Patients received chronic hemodialysis, gastrointestinal diseases (long-term diarrhea, stomach or ileectomy), tuberculosis, cancer, ulcer disease, hyperthyroidism, fever, infection, trauma, burns, surgery, etc;
(2) Patients who receive parenteral nutrition due to strict control or dietary choices may experience sudden weight loss due to malnutrition, as well as during pregnancy and lactation;
(3) When barbiturates, tetracyclines, salicylic acids, or vitamin C are used as acidifiers of the urinary system.
[Specification]5ml:0.5g
[Usage dosage]Intramuscular or intravenous injection, 0.1-0.25g per dose in adults, 1-3 times daily; Children should receive 0.1-0.3g daily injections in small doses, and large doses can be used to treat Keshan disease at the discretion of the physician.
[Adverse reactions]1. Long term use of 2-3 grams per day can cause scurvy after discontinuation of medication. 2. Long term use of a large amount of vitamin C can occasionally cause urate, cysteine, or oxalate stones. 3. Rapid intravenous injection can cause dizziness and fainting.
[Taboo]This experiment was not conducted and there are no reliable references available.
[Precautions]
1. The role of vitamin C in preventing or treating cancer, gingivitis, suppuration, bleeding, hematuria, retinal bleeding, depression, dental caries, anemia, acne, infertility, aging, arteriosclerosis, ulcer disease, tuberculosis, dysentery, collagen related diseases, fractures, skin ulcers, hay fever, drug poisoning, vascular embolism, colds, etc. has not been proven.
2. Interference with diagnosis. The extensive application will affect the results of the following diagnostic tests:
(1) Stool occult blood can cause false positives;
(2) It can interfere with the automatic analysis results of serum lactate dehydrogenase and serum transaminase concentration;
(3) Urinary sugar (copper sulfate method) and glucose (oxidase method) can both cause false positives;
(4) Elevated concentrations of oxalate, urate, and cysteine in urine;
(5) The concentration of serum bilirubin decreased;
(6) Urine pH decreases.
3. The following situations should be used with caution:
(1) Cysteineuria;
(2) Gout;
(3) Hyperoxaluria;
(4) Oxalate deposition syndrome;
(5) Uric acid salt induced kidney stones;
(6) Diabetes (because vitamin C may interfere with blood glucose quantification);
(7) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency;
(8) Hemochromatosis;
(9) Iron granulocytic anemia or thalassemia;
(10) Sickle cell anemia.
4. Taking a large amount of medication for a long time and suddenly stopping the medication may cause symptoms of scurvy, so it is advisable to gradually reduce the dosage and stop the medication.
[Medication for pregnant lactating women]This product can pass through the placenta and be secreted into milk. When pregnant women take large doses, they can develop infantile sepsis.
[Children's medication]This experiment was not conducted and there are no reliable references available.
[Elderly medication]This experiment was not conducted and there are no reliable references available.
[Drug interactions]
1. High doses of vitamin C can interfere with the anticoagulant effect of anticoagulants.
2. When used in combination with barbiturates or propafenone, it can promote the excretion of vitamin C.
3. Sodium cellulose can promote the metabolism of vitamin C to oxalate.
4. Long term or extensive use of vitamin C can interfere with the effect of disulfiram on ethanol.
5. Salicylic acids can increase the excretion of vitamin C.
6. It is not suitable to mix with alkaline drugs (such as aminophylline, sodium bicarbonate, sodium glutamate, etc.), riboflavin, trichlorobutanol, copper, and iron ions (in trace amounts) to avoid affecting the therapeutic effect.
7. When combined with vitamin K3, the latter has oxidizing properties and can produce redox reactions, weakening or disappearing their therapeutic effects.
[Drug overdose]1-4g daily can cause diarrhea, rash, increased gastric acid, and gastric reflux. In some cases, urinary stones, increased excretion of oxalate and urate salts in the urine, deep vein thrombosis, intravascular hemolysis or coagulation can be seen, sometimes leading to a decrease in white blood cell phagocytosis. When the daily dosage exceeds 5g, it can cause hemolysis, and in severe cases, it can be fatal. When used extensively by pregnant women, it can lead to infantile scurvy.
[Pharmacology toxicology]This product is a vitamin based medicine. Vitamin C is involved in amino acid metabolism, neurotransmitter synthesis, collagen synthesis, and interstitial tissue synthesis. It can reduce the permeability of capillaries, accelerate blood coagulation, stimulate coagulation function, promote iron absorption in the intestine, promote blood lipid reduction, increase resistance to infection, participate in detoxification function, and have anti histamine effects and prevent the generation of carcinogens (nitrosamines).
[Pharmacokinetics]The protein binding rate is low. A small amount is stored in plasma and cells, with the highest concentration in glandular tissue. Intrahepatic metabolism. Very few are excreted through the kidneys as prototypes or metabolites, when the plasma concentration is greater than 14 μ At g/ml, the urine output increases. It can be cleared through hemodialysis.
[Storage]Shading and sealed storage. The preparation should not be applied after its color turns yellow.
[Packaging]Ampoule packaging, 5 pieces/box
[Validity period]18 months
[Executive Standards]Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2010 Edition Part 2
[Approval number]National Pharmaceutical Standards H33021541
[Manufacturing enterprise]
Enterprise Name:Zhejiang Cheng Yi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Production Address: No.118 Huahua Road, Dongtou County, Zhejiang Province, China
Phone number:86-0577-6348-3979
Fax number:86-0577-6348-5135
Website:en.chengyipharma.com