[Drug Name]
Common name: Lidocaine Hydrochloride Injection
[Ingredients]
Main ingredient: lidocaine hydrochloride
Chemical name: N - (2,6 dimethylphenyl) -2 (diethylamino) acetamide hydrochloride hydrate.
Chemical structural formula: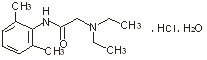
Molecular formula: C14H22N2O · HCI · H2O
Molecular weight: 288.82
All auxiliary materials: sodium chloride, dilute hydrochloric acid.
[Character]This product is a colorless and clear liquid.
[Indications]This product is a local anesthetic and antiarrhythmic drug. It is mainly used for infiltration anesthesia, epidural anesthesia, surface anesthesia (including mucosal anesthesia during thoracoscopy or abdominal surgery), and nerve conduction block. This product can be used for ventricular premature beats and ventricular tachycardia after acute myocardial infarction, as well as for digitalis poisoning, cardiac surgery, and ventricular arrhythmias caused by cardiac catheters. This product is usually ineffective in treating supraventricular arrhythmias.
[Specification]5ml:0.1g
[Usage dosage]
1. Anesthesia
(1) Adult usage:
① Surface anesthesia: A 2% to 4% solution should not exceed 100mg (1 tube) at a time. When administered by injection, the dosage should not exceed 4.5mg/kg (without adrenaline) or every 7mg/kg (with adrenaline at a concentration of 1:200000).
② Sacral canal block for labor analgesia: Use 1.0% solution, limited to 200mg.
③ Epidural block: Use a solution of 1.5% to 2.0%, 250-300mg, in the thoracolumbar region.
④ Infiltration anesthesia or intravenous block: Use 0.25% -0.5% solution, 50-300mg.
⑤ Peripheral nerve block: Brachial plexus (unilateral) with 1.5% solution, 250-300mg; Dental 2% solution, 20-100mg; Use 1% solution for intercostal nerves (each branch), limited to 30mg and 300mg; Use 0.5% to 1.0% solution for cervical infiltration, 100mg on both sides; Paravertebral spinal nerve block (each branch) is limited to 1.0% solution, 30-50mg, and 300mg; Use 0.5% to 1.0% solution for the perineal nerve, 100mg on both sides.
⑥ Sympathetic ganglion block: 1.0% solution for cervical stellate nerve, 50mg; 1.0% solution for lumbar anesthesia, 50-100mg.
⑦ One dose limit: 200mg (4mg/kg) without adrenal gland, 300-350mg (6mg/kg) with adrenaline; Intravenous regional blockade, with a maximum of 4mg/kg; Therapeutic intravenous infusion, with an initial dose of 1-2mg/kg and a maximum dose of 4mg/kg. Adult intravenous infusion is limited to 1mg per minute; Repeated administration, with an interval of no less than 45-60 minutes.
(2) Common dosage for children: It varies from individual to individual, and the total amount administered at a time should not exceed 4.0-4.5mg/kg. 0.25% -0.5% solution is commonly used, and only 1.0% solution is used in special circumstances.
2. Anti arrhythmias:
(1) Commonly used quantity
① Intravenous injection: 1-1.5mg/kg body weight (usually 50-100mg) is used as the initial load for 2-3 minutes. If necessary, repeat intravenous injection 1-2 times every 5 minutes, but the total amount within 1 hour should not exceed 300mg.
② Intravenous infusion: Generally, 5% glucose injection is used to prepare 1-4mg/ml of drug solution for infusion or administered with an infusion pump. After using the load, intravenous infusion can continue at a rate of 1-4mg/minute, or at a rate of 0.015-0.03mg/kg body weight per minute. For the elderly, heart failure, cardiogenic shock, decreased liver blood flow, or liver or kidney dysfunction, the dosage should be reduced to 0.5-1mg intravenous drip per minute. You can use a 0.1% solution of this product for intravenous drip, with a maximum of 100mg per hour.
(2) Maximum intravenous injection: The maximum load within 1 hour is 4.5mg/kg body weight (or 300mg). The maximum maintenance amount is 4mg per minute.
[Adverse reactions]
(1) This product can act on the central nervous system, causing adverse reactions such as drowsiness, sensory abnormalities, muscle tremors, convulsions, coma, and respiratory depression.
(2) Can cause hypotension and bradycardia. If the concentration of the drug in the blood is too high, it can cause atrial conduction velocity to slow down, atrioventricular block, inhibit myocardial contractility and decrease cardiac output.
[Taboo]
(1) Prohibited for those who are allergic to local anesthetics;
(2) Patients with Ayers syndrome (acute cardiogenic cerebral ischemia syndrome), preexcitation syndrome, and severe heart conduction block (including sinus, atrioventricular, and intraventricular conduction blocks) are not allowed to use veins.
[Precautions]
(1) Prevent accidental entry into blood vessels and pay attention to the diagnosis and treatment of local anesthetic poisoning symptoms.
(2) Patients with liver and kidney dysfunction, decreased liver blood flow, congestive heart failure, severe myocardial damage, hypovolemia, and shock should use it with caution.
(3) Individuals who are allergic to other local anesthetics may also be allergic to this product, but there have been no reports of cross allergic reactions between lidocaine, procaine amine, or quinidine.
(4) Strictly control the concentration and total dosage of this product. Overdosage can cause seizures and sudden cardiac arrest.
(5) Its metabolism in the body is slower than that of procaine and has a cumulative effect, which can cause poisoning and seizures.
(6) Some diseases, such as acute myocardial infarction, are often accompanied by α The increase in acidic protein and protein rate, as well as the increase in lidocaine protein binding, resulted in a decrease in free blood drug concentration.
(7) During the medication period, attention should be paid to checking blood pressure, monitoring electrocardiogram, and preparing rescue equipment; If the P-R interval of the electrocardiogram is prolonged or the QRS wave is widened, and other arrhythmias or existing arrhythmias worsen, medication should be stopped immediately.
[Medication for pregnant lactating women]This product passes through the placenta and binds to fetal protein higher than adults, so it should be used with caution.
[Children's medication]Neonatal medication can cause poisoning, and premature infants have a longer half-life than normal infants (3.16 hours: 1.8 hours), so they should be used with caution.
[Elderly medication]The dosage of medication for elderly people should be adjusted according to their needs and tolerance level, and the dosage for patients over 70 years old should be halved.
[Drug interactions]
(1) With cimetidine and with β Receptor blockers such as propranolol, metoprolol, and nadolol can inhibit the metabolism of lidocaine through the liver, increase the blood concentration of lidocaine, and cause adverse reactions of the heart and nervous system. The dosage of lidocaine should be adjusted, and the blood concentration of lidocaine should be monitored and monitored by electrocardiogram.
(2) Barbiturates can promote the metabolism of lidocaine, and the combination of the two drugs can cause bradycardia and sinus arrest.
(3) When combined with procaine amine, it can produce transient delirium and hallucinations, but it does not affect the blood concentration of this product.
(4) Isopropylepinephrine can increase the total clearance rate of this product by increasing liver blood flow; Norepinephrine can reduce the total clearance rate of this product by reducing liver blood flow.
(5) There are incompatibilities with the following drugs: phenobarbital, sodium thiopental, sodium nitroprusside, mannitol, amphotericin B, ampicillin, methamphetaxel, and sulfamethoxazole sodium.
[Drug overdose]Overdosage can cause seizures and cardiac arrest.
[Pharmacokinetics]This product is an amide type local anesthetic. After blood absorption or intravenous administration, there is a significant biphasic effect of excitation and inhibition on the central nervous system, and there may be no prior excitation. When the blood drug concentration is low, there is pain relief, drowsiness, and an increase in pain threshold; As the dosage increases, the effect or toxicity increases, and there is an anticonvulsant effect at sub toxic blood drug concentrations; When the blood drug concentration exceeds 5 μ G/ml can cause convulsions. At low doses, this product can promote K+efflux within myocardial cells, reduce myocardial autonomy, and have an anti ventricular arrhythmia effect; At the therapeutic dose, there was no significant effect on the electrical activity of myocardial cells, atrioventricular conduction, and myocardial contraction; Further increase in blood drug concentration can cause a slowing down of cardiac conduction velocity, atrioventricular block, inhibition of myocardial contractility, and a decrease in cardiac output.
[Pharmacokinetics]After injection, the tissue distribution of this product is fast and wide, and it can penetrate the blood-brain barrier and placenta. This product has high anesthesia intensity, fast onset, and strong dispersibility. It takes about 2 hours for the drug to be locally eliminated, and the addition of adrenaline can prolong its action time. Most of them are first degraded by liver microsomal enzyme to the intermediate metabolite monoethyl glycine amide xylene, which still has local anesthesia, with increased toxicity. Then, they are hydrolyzed by amidase and excreted in urine. About 10% of the dosage is excreted in its original form, with a small amount appearing in bile.
[Storage]Sealed storage.
[Packaging]Ampoule packaging, 5 pieces/box
[Validity period]24 months
[Executive standards]Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2010 Edition Part 2
[Approval number]National Pharmaceutical Standards H33021429
[Manufacturing enterprise]
Enterprise Name:Zhejiang Cheng Yi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.
Production Address: No.118 Huahua Road, Dongtou County, Zhejiang Province, China
Phone number:86-0577-6348-3979
Fax number:86-0577-6348-5135
Website:en.chengyipharma.com